Insulation for Balconies and Terraces
For illustrative purposes only
U-value Calculator
Start your U-value calculation >Providing useable space on a flat roof is an attractive proposition for many building types. For people living in flats and apartments, a balcony is a way of accessing an outside space without being at ground floor level. Terraces, meanwhile, can serve larger dwellings and commercial spaces, providing a hard-landscaped gathering place for a variety of uses.
Where balconies and terraces sit over a habitable space, they form part of the building’s thermal envelope. They must be suitably insulated to meet targets for energy efficiency, while bearing the additional load associated with being used for more than occasional maintenance access.
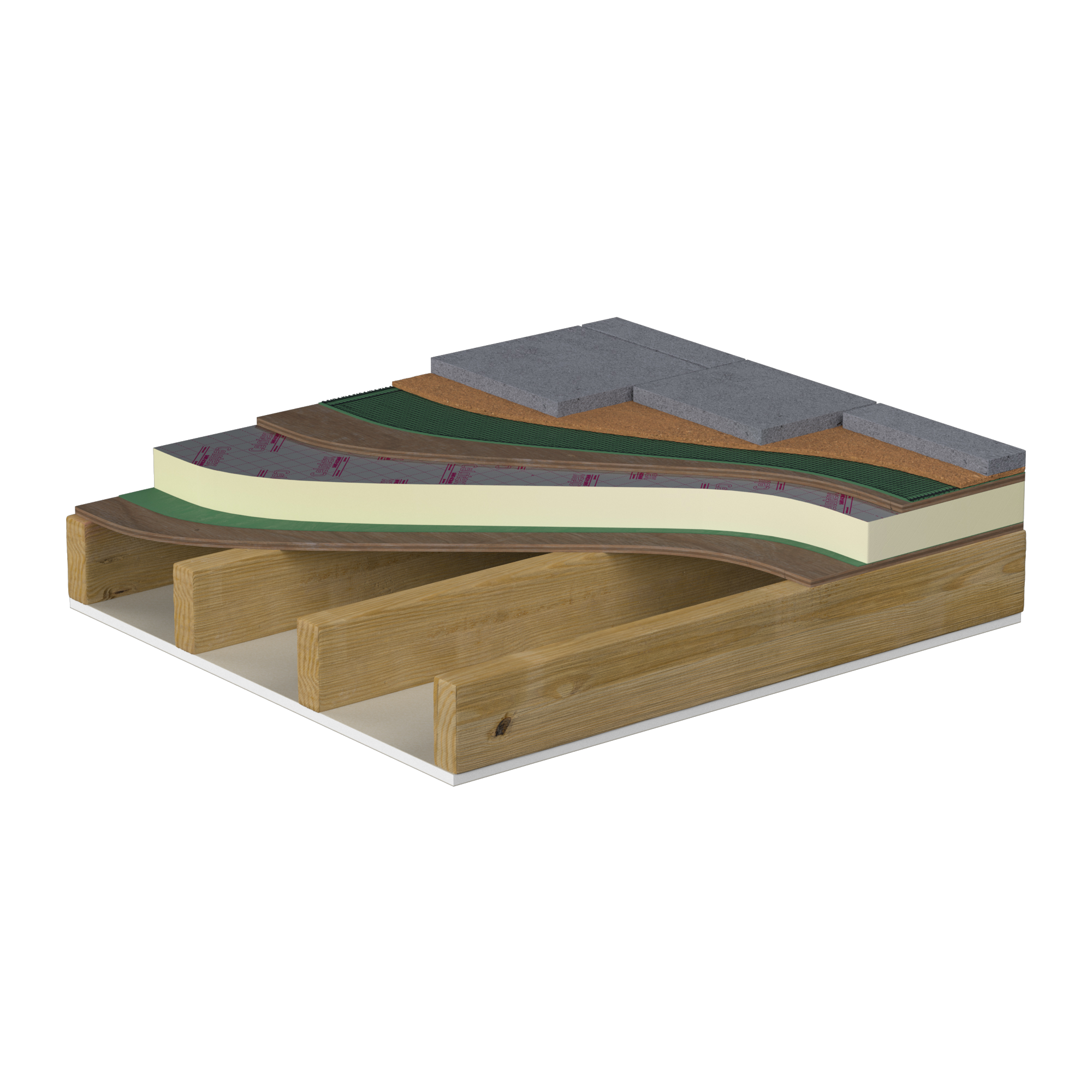
A warm roof design, with insulation (Celotex GA4000 or XR4000 can be considered) laid over the structural timbers, remains the preferred option to a cold roof design. A warm roof does not need cross-ventilation, and lends itself to better detailing at junctions with other elements to address linear thermal bridging.
Celotex rigid polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam boards are lightweight, easy to cut and handle, and can be used to insulate areas of flat roof quickly and efficiently. While they already offer a high compressive strength, to resist the dynamic foot traffic load associated with balconies and terraces, it is recommended to install the boards with an additional layer of plywood over the top. The top layer of ply, like the structural timber deck below the insulation, should be a minimum of 18mm thick. The additional layer protects the insulation from damage, spreading the weight of the decorative roof finish and the extra foot traffic load more evenly throughout the insulation layer.
Unfortunately, Saint-Gobain Interior Solutions does not support the use of its products to insulate between and over the joists of a timber flat roof construction. Approved Document C of the building regulations advises that roof constructions should be in line with British Standard BS5250:2021 Code of practice for control of condensation in buildings.
This document makes provision for 50mm of ventilation to be provided between the underside of the roof deck and the insulation layer in a cold roof situation (where insulation is situated within the structure). It defines a warm roof construction as one where all of the insulation is above the timber joists. For this reason Saint-Gobain Insulation UK does not support a flat roof a hybrid situation with insulation between and above joists. For a flat roof any insulation between joists or below joists would require ventilation to comply with BS5250.
We can provide u-value calculations for either cold or warm flat roofs.
Key Considerations
When using Celotex, you need to satisfy yourself that use of the product meets all relevant national Building Regulations and guidance as well as local, national and other applicable standards relevant for your construction or application, including requirements in relation to fire and applicable height restrictions. In addition to the product datasheet, please refer to the following product documents:
- BBA certificates - where applicable to the application
- Declarations of Performance
- Health & safety datasheets
The building detail is for illustrative purposes only. It does not constitute advice and should not be relied upon.
Insulation products
| Product Name | Thickness Range | Sizes | Lambda |
|---|---|---|---|
| Celotex XR4000 | 110-200mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
| Celotex GA4000 | 50-100mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
| Celotex TB4000 | 20-40mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
| Celotex PL4000 | 25-65mm (+12.5mm Plasterboard) | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
