Insulation for Concrete Slab Floors
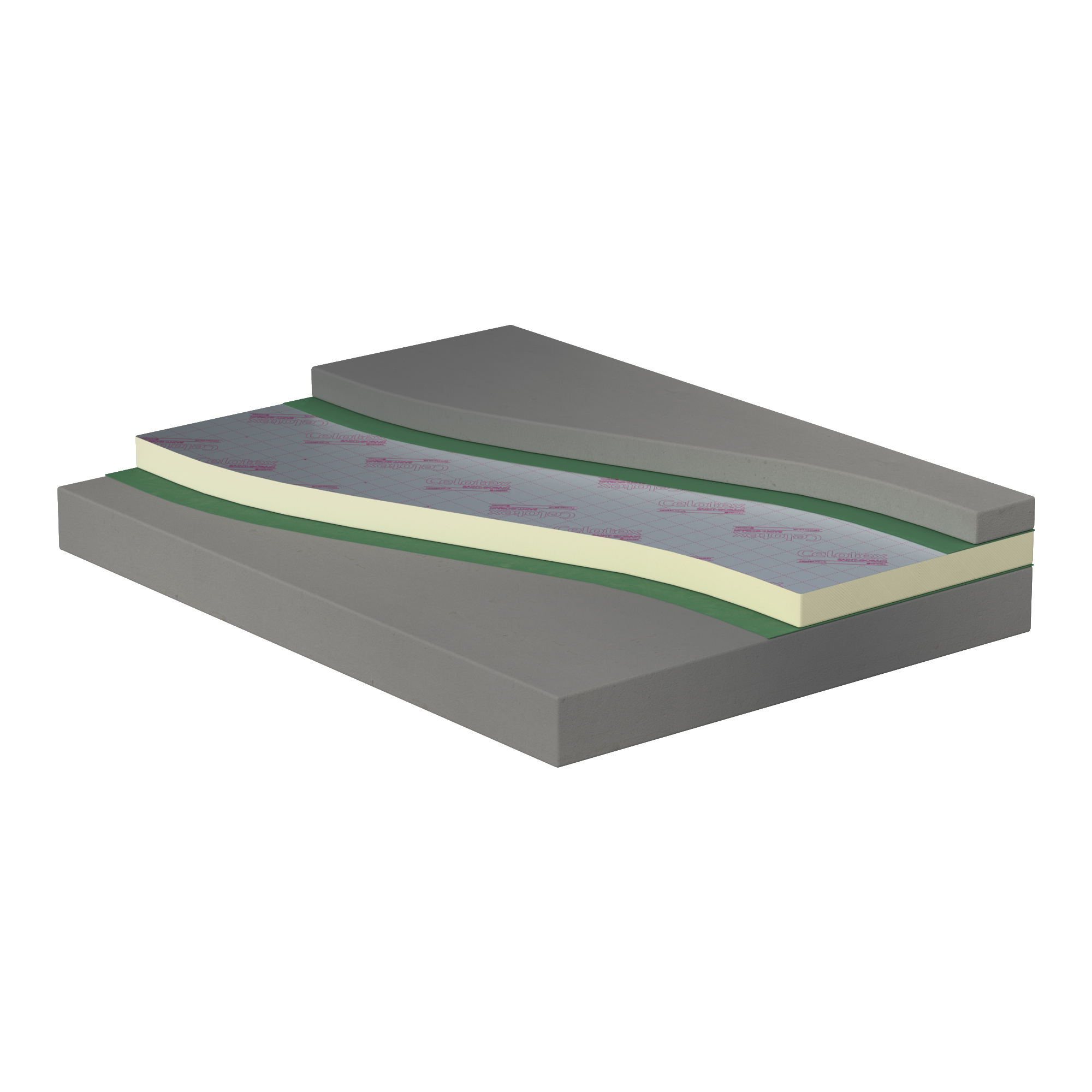
For illustrative purposes only
U-value Calculator
Start your U-value calculationIn a solid or ground-bearing (because it is continuously supported by the ground across its whole area) concrete floor, the choice of insulation position relative to the concrete slab is commonly linked to the building’s heating system.
Insulation below the slab suits continuous, low level heating, gradually warming the thermal mass of the concrete and sustaining it at a consistent temperature. Where the heating is likely to be turned on and off, such as in new-build domestic properties, and a faster thermal response is required, the ‘floating floor’ arrangement of insulation above the slab can be more appropriate. The sub-floor is prepared using well-compacted hardcore and a layer of sand blinding.
- If the insulation is going below the slab, the damp proof membrane (DPM) is laid next, followed by the insulation, a polythene separating layer, and the concrete slab. Depending on the use of the building, the slab can then be finished ready for use, or receive a screed suitable for a floor finish.
- Where insulation is positioned above the slab, the slab and DPM can be installed either way round. The insulation is then laid, followed by a polythene separating layer, and either a concrete screed or tongue and groove chipboard, ready to receive the specified floor finish.
Lightweight, rigid polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam insulation boards (such as Celotex GA4000 and XR4000), are among the most thermally efficient, commonly available insulation materials. They keep the depth of the floor construction down, meaning less excavation, and are easily handled and laid to quickly insulate large areas. Thinner polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam insulation boards, such as Celotex TB4000, can be considered for the perimeter upstand insulation.
For low-rise buildings on poor ground, the floor slab can be designed as a ‘raft’ to act as the foundation. While Celotex PIR boards have a good compressive strength, they cannot be laid below a raft slab and take the structural load of the building. They can, however, be installed above the raft slab, in the same arrangement as described above. For non-domestic uses you should seek the advice of a structural engineer regarding the suitability of any insulation product in a specific floor system.
In a solid or ground-bearing (because it is continuously supported by the ground across its whole area) concrete floor, the choice of insulation position relative to the concrete slab is commonly linked to the building’s heating system.
Key Considerations
When using Celotex products, you need to satisfy yourself that use of the product meets all relevant national Building Regulations and guidance as well as local, national and other applicable standards relevant for your construction or application, including requirements in relation to fire and applicable height restrictions. In addition to the product datasheet, please refer to the following product documents:
- BBA certificates - where applicable to the application
- Declarations of Performance
- Health & safety datasheets
The building detail is for illustrative purposes only. It does not constitute advice and should not be relied upon.
Insulation products
| Product Name | Thickness Range | Sizes | Lambda |
|---|---|---|---|
| Celotex XR4000 | 110-200mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
| Celotex GA4000 | 50-100mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
| Celotex TB4000 | 20-40mm | Width 1200mm, Length 2400mm | 0.022 |
